Toe joint pain is a common condition that affects individuals of all ages, often resulting from injuries, overuse, or chronic conditions such as arthritis and gout. The toes are essential for maintaining balance, supporting body weight, and facilitating movement, so any discomfort in these joints can severely impact daily activities like walking, running, or standing. Early recognition of symptoms, including swelling, stiffness, redness, or limited motion, is vital to manage toe joint pain effectively.
Repetitive stress from tight footwear, high-impact activities, or prolonged standing can contribute to inflammation and pain in the toe joints. Additionally, structural issues such as bunions or misaligned toes may worsen discomfort over time. Understanding the root causes of toe pain helps in choosing appropriate treatments, whether through rest, therapy, or lifestyle modifications.
Managing toe joint pain requires a comprehensive approach that combines physical therapy, supportive footwear, anti-inflammatory diet, and targeted exercises. By adopting preventive strategies and seeking timely medical care, individuals can reduce pain, enhance mobility, and maintain healthy toe joints for long-term comfort and function.
What is Toe Joint Pain ?
Toe joint pain refers to discomfort, stiffness, or swelling in one or more toe joints, affecting mobility and daily activities. It can arise suddenly due to injuries like stubbing, fractures, or sprains, or develop gradually from degenerative conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Pain may be felt at the base, middle, or tip of the toes, and can range from mild irritation to severe, disabling discomfort. Recognizing the type and location of toe pain is crucial for proper management and treatment.
Common causes of toe joint pain include bunions, gout, arthritis, and repetitive strain injuries like turf toe. These conditions often lead to inflammation, reduced flexibility, and difficulty in walking or standing. Symptoms such as redness, swelling, or warmth indicate an active inflammatory process, signaling the need for timely care. Early diagnosis helps prevent long-term complications and joint deformities.
Effective management of toe joint pain involves a combination of rest, supportive footwear, exercises, anti-inflammatory measures, and medical interventions when necessary. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding activities that strain the toes, further support joint health. Understanding the underlying cause allows for targeted treatment, improved mobility, and long-term relief from discomfort.
Why Toe Joint Pain Occurs
Toe joint pain occurs due to a combination of mechanical, inflammatory, and degenerative factors. Overuse or repetitive stress from activities like running, dancing, or standing for long periods can strain the joints and surrounding tissues. Injuries such as stubs, fractures, or sprains directly damage joint structures, leading to acute pain. Chronic conditions, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gout, cause inflammation, cartilage degeneration, and joint swelling, which contribute to persistent discomfort. Poor footwear or high heels can also misalign toes, increasing pressure and causing pain over time.
Infections and metabolic disorders like diabetes or uric acid buildup may also trigger joint inflammation. Inflammation leads to redness, swelling, and stiffness, making walking or standing difficult. Understanding why toe pain develops is essential for prevention and selecting the right treatment to restore mobility and reduce long-term complications.
Early identification of triggers, whether lifestyle-related or medical, can help manage pain before it worsens.
How Toe Joint Pain Develops
Toe joint pain develops when the delicate structures of the toes—including bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage—are stressed, inflamed, or damaged. Injuries like fractures, sprains, or turf toe immediately disrupt normal joint function, causing sharp, localized pain. Repetitive strain over time weakens connective tissues, resulting in chronic discomfort. Conditions such as arthritis degrade cartilage, leading to friction between bones and inflammation, which intensifies pain with movement.
Inflammatory responses in the joints cause swelling, heat, and stiffness, reducing flexibility. Over time, untreated pain can lead to deformities, restricted mobility, or compensatory walking patterns that strain other joints. Improper footwear or biomechanical imbalances worsen the stress on the toes, further aggravating toe joint pain.
By understanding how toe joint pain develops, individuals can adopt preventive measures, such as strengthening exercises, supportive shoes, and anti-inflammatory strategies, to maintain healthy toe joints and minimize long-term damage.
When Toe Joint Pain Needs Attention
Toe joint pain should be monitored carefully to determine when medical intervention or lifestyle changes are necessary. Mild pain may resolve with rest, ice therapy, or adjustments in footwear, but persistent or worsening pain signals the need for professional evaluation. If pain occurs after an injury, appears suddenly, or is accompanied by swelling, redness, or bruising, immediate attention is recommended to rule out fractures or ligament damage.
Chronic toe joint pain that interferes with walking, balance, or daily activities should also prompt medical assessment. People with underlying conditions like arthritis, gout, or diabetes must monitor toe health closely, as untreated inflammation can cause permanent joint damage. Early consultation allows for diagnostic imaging, lab tests, and tailored treatment plans, preventing complications.
Causes of Toe Joint Pain
Toe pain can result from multiple factors. Trauma or injury, such as stubbing your toe or dropping a heavy object, can cause acute pain. Repetitive stress from activities like running, dancing, or wearing tight shoes may lead to chronic issues. Medical conditions like arthritis, gout, or bunions also contribute to inflammation and stiffness. Understanding the root cause is crucial for effective management of toe joint pain.
Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis cause inflammation, stiffness, and swelling in toe joints.
Gout: Uric acid buildup can lead to sudden, severe pain, particularly in the big toe.
Injury: Sprains, fractures, or stubbed toes can damage joints and ligaments.
Overuse: Repetitive movements like running, dancing, or prolonged standing stress the toes.
Footwear: Tight or poorly fitted shoes can cause bunions, corns, and joint misalignment.
Infection: Bacterial or fungal infections can lead to painful, swollen toe joints.
Symptoms of Toe Joint Pain
Simple home remedies can provide relief from mild toe pain. Ice or heat therapy reduces swelling and soreness, while massage increases blood flow and relaxes tight muscles. Elevating the foot helps reduce inflammation, especially after long periods of standing or activity.
Swelling and redness around the joint
Stiffness and reduced mobility
Sharp, throbbing, or aching pain
Difficulty walking or balancing
Visible deformities like bunions or hammer toes
Top Tips for Managing Toe Joint Pain
Rest and Foot Elevation
Resting your feet is crucial when managing toe joint pain, as it reduces inflammation and allows damaged tissues to heal. Avoid standing for long periods or performing activities that strain your toes. Simple lifestyle adjustments, like sitting with your feet elevated, can drastically reduce swelling and discomfort.
Elevating your foot on pillows or cushions above heart level improves blood circulation and prevents fluid accumulation in the affected toe joints. This reduces pressure and promotes faster healing. Proper rest ensures that inflamed tissues are not subjected to additional stress, which is essential for effective recovery.
Using supportive footwear and cushioned footrests while resting adds extra comfort and protection. By incorporating rest and elevation consistently, individuals suffering from toe pain can manage symptoms effectively, minimize flare-ups, and support long-term joint health.
Benefits:
Reduces inflammation
Prevents further injury
Speeds up recovery
Ingredients for Rest:
Cushioned footrests
Supportive pillows
Comfortable footwear
Apply Ice or Heat Therapy
Ice therapy is one of the most effective ways to manage acute toe pain, especially after injury or intense activity. Applying ice packs for 15–20 minutes reduces swelling, numbs pain, and controls inflammation. Cold therapy should be used multiple times a day during the early stages of discomfort.
Once inflammation has decreased, heat therapy can help relieve stiffness and improve flexibility. Warm compresses or heating pads applied to the toes relax tense muscles, enhance blood flow, and soothe soreness. Alternating between ice and heat can accelerate recovery and provide long-lasting relief.
Using soft towels to protect skin and prevent frostbite during ice application is recommended. Combining these methods helps manage toe joint pain effectively, allowing individuals to continue daily activities while promoting healing and comfort.
Benefits:
Reduces swelling and soreness
Improves blood flow
Relieves stiffness
Therapy Ingredients:
Ice packs or frozen gel packs
Warm compress or heating pad
Soft towels
Foot and Toe Exercises
Targeted foot and toe exercises play a critical role in relieving toe pain and preventing recurrence. Stretching exercises like toe extensions, towel scrunches, and picking up small objects with toes enhance flexibility and strengthen the muscles surrounding the joints.
Daily exercise improves blood flow, reduces stiffness, and maintains proper alignment of the toes. Strengthening the supporting muscles also decreases the strain on toe joints during walking, running, or standing. A consistent routine helps reduce the risk of chronic pain and joint deformities.
Tools like resistance bands, small balls, or towels for scrunch exercises can make these routines more effective. Incorporating foot exercises into a daily regimen significantly improves mobility and comfort for those suffering from toe joint pain.
Benefits:
Enhances joint flexibility
Strengthens supporting muscles
Prevents chronic pain
Exercise Ingredients:
Resistance bands
Small balls or marbles
Towel for scrunch exercises
Use Proper Footwear
Wearing supportive footwear is essential in managing toe pain. Shoes that fit well, have cushioned soles, and wide toe boxes reduce pressure on affected joints and prevent deformities like bunions or hammer toes. Avoid tight, pointed, or high-heeled shoes that compress toes and worsen pain.
Orthopedic inserts or cushioned insoles can provide additional support, improve alignment, and distribute pressure evenly across the foot. Proper footwear minimizes stress during walking, running, or standing, which accelerates recovery and prevents flare-ups.
Investing in the right shoes and periodically checking fit ensures long-term protection of toe joints. Consistent use of appropriate footwear is one of the most effective strategies to alleviate toe pain and maintain healthy feet.
Benefits:
Reduces pressure on joints
Prevents deformities
Supports proper alignment
Footwear Ingredients:
Wide toe box shoes
Orthopedic inserts
Cushioned soles
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
A nutritious, anti-inflammatory diet can significantly improve symptoms of toe joint pain. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin C, vitamin D, calcium, and antioxidants help reduce inflammation, strengthen cartilage, and support bone health. Include fatty fish, leafy greens, berries, nuts, and citrus fruits in your daily meals.
Avoid processed foods, excess sugar, and alcohol, as these can trigger inflammation and worsen pain. Proper nutrition not only helps alleviate discomfort but also aids tissue repair, maintains joint function, and prevents long-term degeneration.
A balanced anti-inflammatory diet complements other pain management strategies. Combining proper nutrition with rest, exercise, and footwear ensures a holistic approach to reducing toe pain and improving overall foot health.
Benefits:
Reduces inflammation naturally
Supports cartilage and joint health
Boosts overall wellness
Diet Ingredients:
Salmon, mackerel
Spinach, kale
Walnuts, almonds
Berries, oranges
Pain Relief Medications
Over-the-counter medications, such as NSAIDs like ibuprofen, are effective for reducing toe joint pain and inflammation. Topical gels or creams applied directly to the affected joints offer targeted relief without systemic side effects. Always consult a healthcare provider before long-term use to avoid complications.
Medications can be especially helpful for flare-ups or when other methods like rest and exercise are insufficient. Short-term use supports mobility and allows individuals to maintain daily activities with less discomfort.
Combining medication with lifestyle interventions like exercise, proper footwear, and diet enhances recovery. Strategic use of pain relief measures ensures that toe pain is managed effectively while supporting overall joint health.
Benefits:
Reduces pain and swelling
Improves mobility
Supports daily activities
Medication Ingredients:
NSAID tablets or gels
Prescription anti-inflammatories
Topical analgesics
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies can provide additional relief for chronic toe joint pain. Acupuncture targets specific pressure points to reduce inflammation and improve circulation, while massage therapy relieves stiffness and promotes relaxation. Hydrotherapy, including warm water exercises, strengthens joints without placing excessive stress on them.
These therapies are complementary to conventional treatments, providing non-invasive ways to manage pain. Regular sessions can enhance flexibility, reduce discomfort, and improve overall foot function.
Incorporating licensed therapists, massage oils, or hydrotherapy pools into a treatment plan ensures safe and effective pain management. Alternative therapies help individuals dealing with toe joint pain achieve long-term relief and improved mobility.
Benefits:
Relieves chronic pain
Enhances blood flow
Improves relaxation
Therapy Ingredients:
Licensed acupuncturist or therapist
Massage oils or gels
Hydrotherapy pool access
Regular Medical Check-Ups

Persistent or severe toe joint pain should be assessed by a healthcare professional. X-rays, MRIs, or blood tests help determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment. Early diagnosis can prevent long-term joint damage and complications.
Medical check-ups also allow monitoring of chronic conditions like arthritis, gout, or tendonitis. Professional guidance ensures that interventions are safe, effective, and tailored to individual needs.
Combining regular medical monitoring with rest, exercise, proper footwear, and dietary adjustments provides a comprehensive approach to managing toe joint pain. Timely medical intervention ensures faster recovery and better long-term joint health.
Benefits:
Tracks joint health
Detects early issues
Provides professional guidance
Check-Up Ingredients:
Doctor consultations
Imaging tests
Blood and uric acid tests
Exercise and Stretching
Gentle toe exercises improve flexibility, strengthen supporting muscles, and reduce stiffness. Exercises like toe curls, towel scrunches, and picking up objects with toes help maintain joint health. Stretching before and after activity reduces the risk of injury and alleviates discomfort, making it a critical part of managing toe joint pain.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Nutrition plays an important role in joint health. Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish and flaxseeds), antioxidants (berries, citrus fruits), and calcium-rich foods (dairy, leafy greens) reduce inflammation and support bone and joint repair. Limiting processed foods, sugars, and alcohol further helps manage toe joint pain effectively.
Preventive Measures for Toe Joint Pain
Avoid repetitive strain on toes
Stretch before and after physical activity
Wear supportive footwear
Maintain healthy weight to reduce joint pressure
Practice foot hygiene and proper care
Conclusion
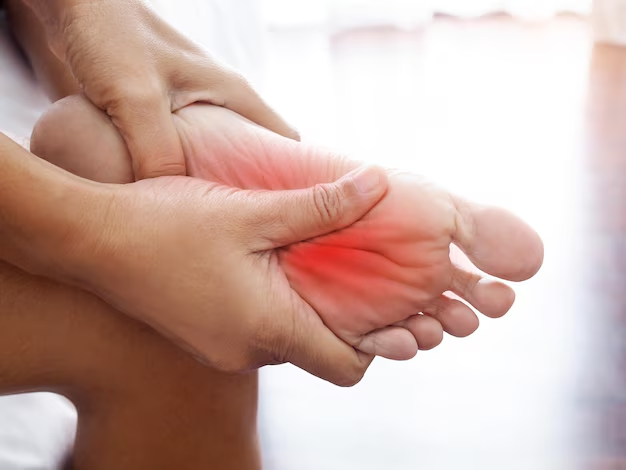
Toe joint pain can significantly impact daily activities, making walking, standing, and exercising uncomfortable. Understanding the causes—such as injuries, arthritis, bunions, gout, or repetitive stress—is essential for effective management. Early intervention with rest, proper footwear, and supportive measures can help alleviate discomfort and prevent further damage. Addressing toe joint pain promptly ensures better mobility and reduces the risk of chronic issues over time.
In addition to rest, targeted exercises and stretches strengthen the muscles supporting the toes and improve joint flexibility. An anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega-3s, leafy greens, and nuts supports joint health, while medications or topical treatments may provide short-term relief from pain and swelling. Alternative therapies like massage, acupuncture, or hydrotherapy can complement conventional care, offering enhanced comfort and improved circulation. These strategies collectively help manage toe joint pain effectively.
Regular medical check-ups and preventive practices are crucial for long-term toe health. By monitoring symptoms and addressing issues early, individuals can maintain healthy toe joints, reduce recurrence, and enjoy an active, comfortable lifestyle. Combining lifestyle modifications with professional guidance ensures that toe joint pain does not hinder daily activities or overall quality of life.
FAQs
Q1. What are common causes of toe joint pain?
Injury, arthritis, gout, bunions, overuse, and infection are frequent causes.
Q2. Can toe joint pain heal naturally?
Yes, with rest, exercises, proper footwear, diet, and lifestyle modifications.
Q3. Are braces effective for toe joint pain?
Yes, they provide support, reduce strain, and aid recovery.
Q4. Which foods help reduce toe joint pain?
Omega-3 fatty acids, leafy greens, nuts, berries, and fatty fish support joint health.
Q5. When should I see a doctor for toe pain?
Seek medical care if pain is severe, persistent, or limits walking and daily activities.

