Sexual health plays a vital role in a person’s overall well-being. It covers more than just physical aspects—it also includes emotional, mental, and social well-being. A healthy approach to sexuality means being informed, safe, and respectful in all sexual activities and relationships. Good sexual health allows people to have pleasurable and safe experiences without fear, shame, or harm.
One of the key parts of sexual health is understanding how to protect oneself from sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies. This includes practicing safe sex, using protection, and getting regular check-ups. Education about the human body, reproductive systems, and personal boundaries also helps people make better decisions about their sexual behavior.
Maintaining sexual health also involves open communication, mutual consent, and respect in relationships. When people feel emotionally and mentally secure, they’re more likely to build strong, healthy sexual connections. Learning about consent, boundaries, and trust is essential to every healthy relationship.
What is Sexual Health ?

Sexual health, as defined by the World Health Organization (WHO), is a state of physical, emotional, mental, and social well-being in relation to sexuality. It goes beyond just avoiding illness or dysfunction. Instead, it focuses on a complete and positive approach to sexual experiences. This includes having access to accurate information, safe practices, and support in making informed choices.
True sexual health means respecting yourself and others, having mutual understanding in relationships, and feeling confident in your decisions about sexual activity. It involves being able to communicate openly, give and receive consent, and maintain personal boundaries. Achieving sexual health also includes access to education and healthcare, which helps individuals make responsible choices and develop healthy relationships throughout their lives.
Key Components of Sexual Health:
Physical Health:
Taking care of physical sexual health means preventing and treating infections, such as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), using protection during sexual activity, and keeping the reproductive system healthy. This also includes regular health check-ups and practicing safe sex to avoid unwanted pregnancies and illnesses.
Emotional Health:
Emotional well-being involves understanding your own feelings, desires, and personal boundaries. It also includes being able to express emotions in a healthy way and building strong, respectful relationships based on trust and care.
Psychological Health:
This part of sexual health focuses on the mental side of sexuality, such as having a positive body image, understanding your sexual identity, and feeling good about yourself. It also involves dealing with stress or concerns about sex in a healthy, supportive way.
Social Well-being:
Social sexual health means having respectful and consensual relationships with others. It also includes living in a society that values sexual rights, supports open communication, and respects personal choices.
The Importance of Sexual Education
Sexual education plays a key role in supporting and promoting sexual health. When people have access to clear and accurate information, they are more likely to make safe and responsible choices that protect both their own well-being and that of others. Education helps individuals understand their bodies, know the risks involved in sexual activity, and learn how to prevent issues like sexually transmitted infections and unplanned pregnancies.
Starting sexual education at an early age is important. It should cover not just the physical side of sex, but also the emotional and social parts. Young people need to learn about respect, consent, personal boundaries, and healthy relationships. When they are properly informed, they gain confidence and are better prepared to manage their sexual health in a responsible and respectful way throughout their lives.

Benefits of Sexual Education:
Increased Awareness of STIs and Prevention: Learning about contraception and how to prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) helps people make safer choices. This knowledge can lead to fewer unplanned pregnancies and lower the risk of spreading infections. Understanding how to use protection and when to seek medical help is an important part of protecting one’s sexual health.
Promotes Healthy Relationships: Sexual education teaches important values like respect, consent, and open communication. These lessons help individuals build strong, trusting, and respectful relationships. When people understand boundaries and the importance of mutual agreement, they are more likely to have healthy and safe connections with others.
Helps Reduce Stigma: Education helps people talk more openly about topics like menstruation, sexual orientation, and reproductive health. This can reduce shame, confusion, and fear. As more people become informed, it creates a more inclusive and supportive society for everyone.
Key Topics in Sexual Education:
Anatomy and reproductive systems
Contraception and family planning
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Consent and communication
Gender identity and sexual orientation
Emotional aspects of sexuality
Reproductive Health: A Core Aspect of Sexual Health
Reproductive health is an important part of sexual health. It involves the proper functioning of the reproductive systems and the ability to enjoy a safe and satisfying sexual life. It also means having access to the information and services needed to make informed choices about reproduction.
This includes areas such as fertility, birth control, pregnancy, and safe childbirth. Reproductive health supports individuals in planning their families and caring for their bodies. When people understand their reproductive health, they are better able to protect themselves and improve their overall sexual health and well-being throughout different stages of life.
Contraception: Contraception is a key part of reproductive and sexual health because it helps people plan when or if they want to have children. There are many types of birth control available. Hormonal methods include pills, patches, and injections that help prevent pregnancy by changing hormone levels. Barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms stop sperm from reaching the egg. Long-acting reversible contraception (LARC), such as intrauterine devices (IUDs) and implants, are effective for several years and require little daily attention, making them a good option for people who want reliable, long-term protection.
Fertility and Infertility: Fertility is the natural ability to have children. Many things can affect fertility, such as age, overall health, lifestyle habits, medical problems, and even inherited conditions. Infertility is when a couple is unable to conceive after trying for a year. This can be emotionally difficult, but help is available. Assisted reproductive technologies (ART), like in vitro fertilization (IVF), can increase the chance of having a baby. Learning about fertility helps people make informed decisions about family planning and their sexual health.
Pregnancy and Childbirth: A healthy pregnancy and safe childbirth are important parts of sexual health. This includes getting regular check-ups, eating a balanced diet, and receiving emotional and physical support during pregnancy. Prenatal care helps monitor both the baby’s and the mother’s health. During labor and delivery, having trained healthcare providers and proper care can reduce risks and improve outcomes for both mother and baby. Support during this time also helps create a positive birth experience.
Understanding and Preventing Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are infections that spread through sexual contact. They can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites and may lead to serious health problems if not treated properly. Some STIs show clear symptoms, while others may go unnoticed for a long time. Understanding how STIs are passed from one person to another is an important part of protecting your sexual health. Using protection, getting regular check-ups, and seeking prompt treatment can help prevent the spread of STIs and support overall sexual health and well-being.
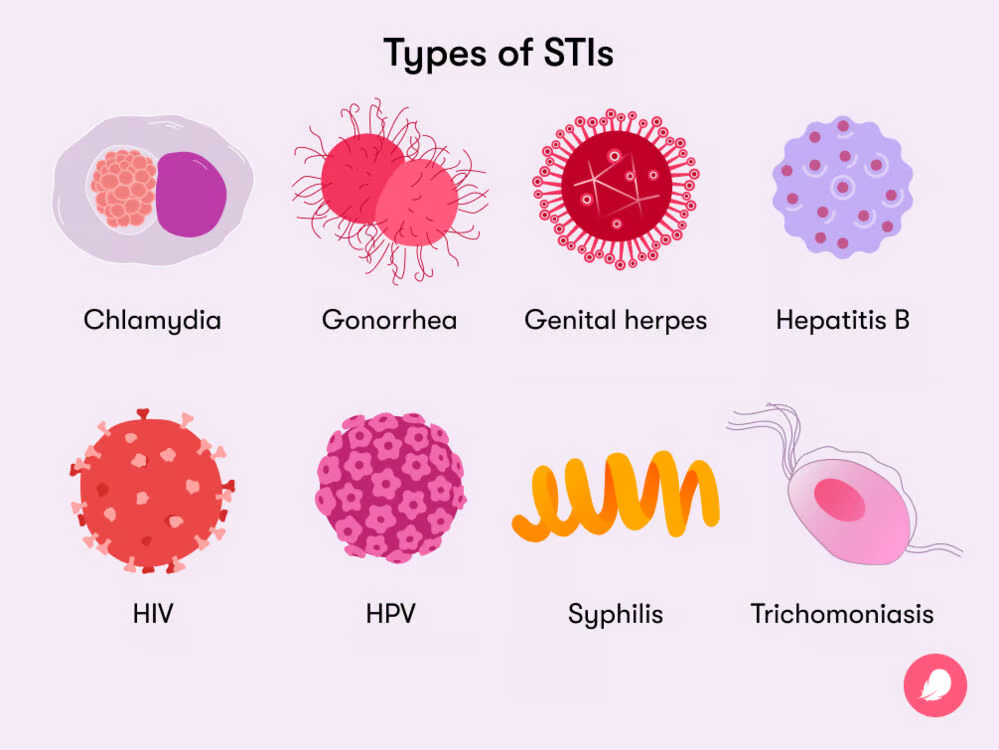
Common STIs:
Chlamydia: Chlamydia is a bacterial infection that often shows no symptoms, making it difficult to detect. If left untreated, it can cause serious complications, including infertility in both men and women. It’s essential to get tested regularly, especially if sexually active, to avoid long-term health issues.
Gonorrhea: Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection that can affect different parts of the body, including the genital tract, throat, and eyes. Like chlamydia, it can be asymptomatic, especially in women, which means it can go unnoticed and cause damage. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent complications.
HIV/AIDS: HIV is a viral infection that weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections and diseases. If left untreated, HIV can progress to AIDS, a condition where the immune system is severely compromised. While there is no cure, early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition and improve quality of life.
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): HSV is a viral infection that causes painful sores or blisters, usually around the genital area or mouth. It is highly contagious, and while there is no cure, antiviral medications can help manage outbreaks and reduce the risk of transmission. Many people with HSV may experience mild symptoms or none at all.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV): HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection, with many people unaware they have it because it often doesn’t show symptoms. Some strains of HPV can cause genital warts, while others are linked to certain cancers, including cervical, anal, and throat cancers. Vaccines are available to protect against the most harmful strains of HPV.
Syphilis: Syphilis is a bacterial infection that develops in stages. The first stage includes painless sores, but if left untreated, it progresses to more severe stages, affecting organs like the heart and brain. It’s important to seek treatment early, as syphilis can cause serious long-term health issues, including damage to the heart, nervous system, and other vital organs.
Prevention of STIs:
Condoms: Male and female condoms are highly effective at reducing the risk of most STIs when used correctly and consistently.
Vaccination: Vaccines are available for some STIs, such as HPV, which can prevent certain cancers and genital warts.
Regular Testing: Regular STI screenings are important for sexually active individuals, especially if they have multiple partners.
Monogamy and Open Communication: Establishing trust, mutual respect, and clear communication with partners can also help reduce the risk of transmission.
The Role of Consent in Sexual Health
Consent is a vital aspect of sexual health and well-being. It involves giving voluntary, enthusiastic, and informed agreement to engage in sexual activity. Consent should be clear and mutual, ensuring that all parties feel comfortable, respected, and empowered in their choices. It’s not just about preventing sexual assault but also about fostering a safe and positive environment where each person has control over their sexual experiences and boundaries.
Understanding and respecting consent helps create healthy sexual relationships, built on trust and communication. Every individual has the right to say “yes” or “no” at any point in time, and these decisions should be respected. By practicing consent, people can protect their sexual health, avoid harmful situations, and ensure that all sexual experiences are safe, consensual, and empowering for everyone involved.
Key Aspects of Consent:
Voluntary: Consent must be given without pressure, manipulation, or coercion.
Informed: All parties must have a clear understanding of what is happening and any potential risks.
Enthusiastic: Consent should be enthusiastic and affirmative, not given out of obligation or hesitation.
Ongoing: Consent can be withdrawn at any time, and all parties should feel free to change their minds
Sexual Health Across the Lifespan
Sexual health is an ongoing journey that evolves throughout a person’s life, from adolescence to adulthood and into old age. Each stage presents its own set of challenges and opportunities for maintaining sexual well-being. In adolescence, it’s important to learn about consent, relationships, and safe sex practices. In adulthood, managing sexual health may involve addressing issues like contraception, fertility, or sexual function. As people age, changes in sexual health can occur, but open communication, self-care, and informed choices can help maintain a fulfilling and healthy sexual life at every stage.
Adolescence and Young Adulthood: This is a critical time for sexual development. Teenagers and young adults often experience curiosity about their sexuality and begin to explore relationships and intimacy. Comprehensive sexual education can empower them to make informed decisions, avoid risky behaviors, and understand the importance of consent and safe sex practices.

Adulthood: As adults, individuals may face issues related to contraception, reproductive health, and sexual satisfaction. Relationships may evolve, and the dynamics of intimacy can change. The importance of maintaining open communication with partners about desires, needs, and boundaries remains critical.
Older Age: Sexuality does not end with age. Older adults may face unique challenges related to sexual health, such as changes in libido, physical health issues, or navigating intimacy after the loss of a partner. However, many older adults continue to have fulfilling sexual relationships and maintain a positive attitude toward sexual health.
Psychological and Emotional Aspects of Sexual Health
Sexual health is closely connected to mental and emotional well-being. Factors such as body image, self-esteem, past trauma, and emotional intimacy can greatly influence a person’s sexual health. Positive emotional health supports healthy sexual experiences, while negative emotions or unresolved trauma may create barriers to intimacy and sexual satisfaction. It’s essential to address both mental and emotional aspects to maintain overall sexual health. By fostering a healthy relationship with oneself and others, individuals can enhance their sexual well-being and experience more fulfilling, respectful connections.
Sexuality and Body Image: Individuals who feel positive about their bodies are more likely to have satisfying sexual experiences. On the other hand, poor body image can lead to sexual dissatisfaction, anxiety, and even avoidance of sexual activity. It is important for individuals to feel comfortable in their own skin and to recognize that attractiveness comes in many different forms.
Sexual Dysfunction: Sexual dysfunction is a common issue that affects many individuals at different stages of life. It may include problems with arousal, orgasm, or pain during sex. Psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, and depression can contribute to sexual dysfunction. Seeking support from a healthcare provider or therapist can help address these issues.
Impact of Trauma: Sexual trauma, including assault or abuse, can have profound and lasting effects on sexual health. It is essential for individuals who have experienced trauma to seek professional support to heal and regain control over their sexual health.
Promoting Sexual Health in Society
Promoting sexual health extends beyond individual behavior and into societal attitudes and norms. It is important for communities to foster a culture of respect, equality, and understanding regarding sexuality. This can be achieved through:
Access to Sexual Health Services: It’s important that everyone has access to essential sexual health services, including STI testing, counseling, and contraception. Ensuring these resources are available helps people make informed decisions and maintain their sexual well-being.
Sexual Rights and Education: Promoting comprehensive sexual education and advocating for sexual rights is crucial for all individuals, regardless of gender, sexual orientation, or socioeconomic background. Education empowers people to understand their rights and make safe, informed choices.
Combating Stigma: Reducing stigma surrounding topics such as STIs, LGBTQ+ rights, and sexual orientation is essential for fostering a more inclusive and supportive society. Breaking down these barriers creates an environment where individuals can openly discuss and address their sexual health without fear or shame.
Conclusion
Sexual health is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, encompassing physical, emotional, and relational dimensions. It includes reproductive health, the prevention of STIs, and the emotional well-being of individuals. A healthy understanding of sexual health leads to better life choices and healthier relationships.

By making informed decisions about sexual health, individuals can enhance their quality of life and build respectful relationships. Awareness of consent, emotional intimacy, and safe sexual practices is essential for fostering positive sexual experiences. It also helps prevent harmful behaviors and protects emotional health.
Access to comprehensive sexual education and healthcare is vital in promoting sexual health. Educating people about their rights, contraception, and safe sex practices ensures they can make informed choices. Reducing stigma around sexual health issues, such as STIs and sexual orientation, helps create a supportive, inclusive society where individuals can address their sexual health without fear or shame.
FAQs
- What is sexual health, and why is it important ?
Answer: Sexual health refers to the physical, emotional, mental, and social well-being related to sexuality. It means having a positive and respectful approach to sex and relationships, which includes the ability to make informed and responsible choices. Sexual health is important because it impacts overall well-being, promotes healthy relationships, and reduces the risks of sexually transmitted infections (STIs), unintended pregnancies, and emotional distress. - How can I prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) ?
Answer: The best ways to prevent STIs include using condoms consistently and correctly, getting vaccinated for preventable infections like HPV, getting tested regularly for STIs (especially if you’re sexually active with multiple partners), and maintaining open communication with your sexual partners about health and STI risks. It’s also important to be aware of any symptoms of STIs and seek prompt medical care if you think you may have been exposed. - What should I know about consent in sexual activity ?
Answer: Consent is a crucial aspect of sexual health. It means that all parties involved in sexual activity agree to it willingly, without pressure, manipulation, or coercion. Consent should be clear, enthusiastic, informed, and ongoing. It’s important to remember that anyone has the right to withdraw consent at any time, and respecting each other’s boundaries is key to a healthy sexual experience. - How can I maintain a healthy sexual relationship with my partner ?
Answer: Maintaining a healthy sexual relationship involves communication, respect, and mutual understanding. Discussing desires, boundaries, and any concerns about sexual health openly with your partner is essential. Trust and emotional connection are also important factors. Regular check-ins with each other about feelings and needs can help ensure both partners feel valued and heard in the relationship. - Is sexual health only about avoiding infections and pregnancy ?
Answer: No, sexual health encompasses much more than just avoiding infections and pregnancy. It also includes emotional and psychological aspects of sexuality, such as feeling comfortable and confident in your body, having positive experiences in relationships, practicing consent, and addressing issues like sexual dysfunction or trauma. It’s about creating an environment where individuals feel empowered, safe, and respected in their sexual lives.

