Sugar Health is a natural supplement designed to support healthy blood sugar levels and promote overall metabolic wellness. This product offers a holistic approach to managing blood sugar, providing a balance of plant-based ingredients that work synergistically to help keep glucose levels stable.
For those who are concerned about the risks of high blood sugar, Sugar Health may serve as a beneficial complement to existing diabetes medications. It can be used alongside your current regimen, potentially enhancing your body’s ability to manage glucose more effectively.

While it’s not a replacement for prescribed diabetes medications, Sugar Health provides an additional option for maintaining blood sugar health. With its natural ingredients, it supports a more balanced lifestyle, which is essential for individuals looking to manage their sugar levels in a safe, non-invasive way.
Top 8 Diabetes Medications
Managing diabetes effectively requires a personalized approach, with diabetes medications playing a key role. These medications help keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range and support the body’s ability to use insulin properly.
Depending on the type of diabetes, lifestyle habits, and overall health, various diabetes medications may be prescribed. Each medication is designed to target specific aspects of blood sugar control.
A well-rounded treatment plan combines medications with healthy eating, regular exercise, and monitoring blood sugar levels. This holistic approach is essential for managing diabetes and reducing the risk of complications over time.
Below are the Top 8 Diabetes Medications, categorized by their class and mechanisms of action.
Metformin (Biguanides)
Metformin is one of the most commonly prescribed diabetes medications for managing Type 2 diabetes. It is considered the first-line treatment and is often prescribed either alone or in combination with other drugs. Metformin works by improving the body’s sensitivity to insulin and reducing the amount of sugar produced by the liver. This helps to keep blood sugar levels in check, making it an essential part of many diabetes management plans.
Mechanism of Action: Metformin works by decreasing the amount of glucose produced by the liver, improving insulin sensitivity in muscle cells, and enhancing glucose uptake into cells. It does not stimulate the pancreas to release more insulin, making it a safe option for most patients.
Benefits:
Weight Neutrality: Metformin is considered a weight-neutral medication, meaning it typically does not lead to weight gain. In fact, some people may experience modest weight loss while using it. This makes it a favorable option for individuals with Type 2 diabetes who are also concerned about managing their weight.
Cardiovascular Benefits: Several studies suggest that metformin may offer protective benefits for the heart. It has been shown to help reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications, making it a valuable choice among diabetes medications for individuals at risk of heart disease.
Low Risk of Hypoglycemia: One of the key benefits of metformin is its low risk of causing hypoglycemia, or dangerously low blood sugar levels. Since metformin does not increase insulin production, it does not typically lead to episodes of low blood sugar, which can be a concern with some other diabetes medications.
Side Effects:
Gastrointestinal Issues: Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and bloating.
Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Long-term use of metformin may reduce vitamin B12 levels.
Ideal For: People with Type 2 diabetes, especially those who are overweight or obese.
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas are a class of diabetes medications that have been used for many years to treat Type 2 diabetes. They are often prescribed when metformin alone is not sufficient to control blood sugar levels. Sulfonylureas work by stimulating the pancreas to produce more insulin, helping to lower blood sugar. These medications are commonly added to a treatment plan when additional support is needed to effectively manage blood sugar levels in individuals with Type 2 diabetes.
Mechanism of Action: Sulfonylureas work by stimulating the pancreas to produce more insulin. This increased insulin release helps lower blood sugar levels, especially after meals.
Common Medications:
Glipizide (Glucotrol)
Glyburide (DiaBeta)
Glimepiride (Amaryl)
Benefits:
Effective for Lowering Blood Sugar: Sulfonylureas are highly effective diabetes medications for reducing blood glucose levels, especially after meals (postprandial). By stimulating the pancreas to release more insulin, they help to lower elevated blood sugar levels, making them an important option for people who need additional control over their blood sugar throughout the day.
Easy to Use: One of the advantages of sulfonylureas is their ease of use. These diabetes medications are typically taken once or twice daily, offering a simple and convenient dosing schedule. This simplicity makes them a popular choice for patients who need a straightforward medication to help manage their Type 2 diabetes.
Side Effects:
Risk of Hypoglycemia: Sulfonylureas increase insulin production, which can lead to low blood sugar, especially if meals are missed or if the dose is too high.
Weight Gain: Some patients may experience weight gain with sulfonylureas.
Ideal For: Individuals with Type 2 diabetes who have not achieved optimal control with metformin alone.
DPP-4 Inhibitors (Gliptins)
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors are a newer class of diabetes medications used to treat Type 2 diabetes. These medications work by boosting the body’s natural ability to regulate blood sugar. DPP-4 inhibitors help increase insulin production when blood sugar is high and reduce the amount of sugar produced by the liver. They provide an effective option for individuals whose blood sugar levels are not well-controlled with other diabetes medications, offering a gentler approach to managing Type 2 diabetes.
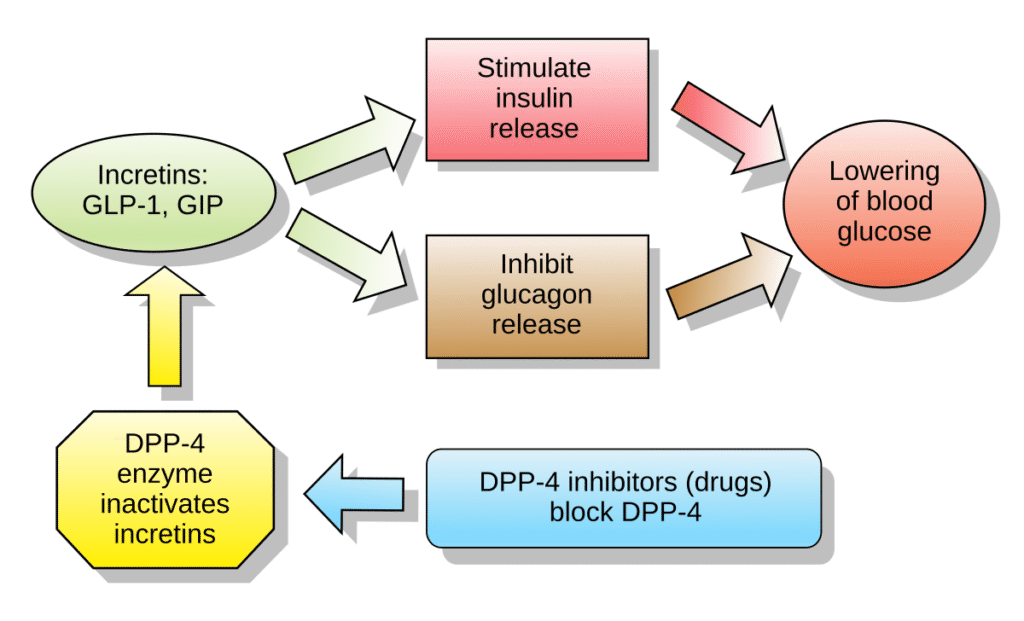
Mechanism of Action: DPP-4 inhibitors work by blocking the enzyme DPP-4, which breaks down incretin hormones. Incretins are hormones that stimulate insulin release and reduce glucose production in the liver. By inhibiting DPP-4, these medications increase insulin secretion and decrease glucose output from the liver.
Common Medications:
Sitagliptin (Januvia)
Saxagliptin (Onglyza)
Linagliptin (Tradjenta)
Benefits:
Minimal Risk of Hypoglycemia: DPP-4 inhibitors carry a low risk of causing hypoglycemia because they work in response to elevated blood sugar levels. They help the body release insulin only when needed, which makes them a safer option for people concerned about low blood sugar episodes.
Weight Neutrality: These diabetes medications are generally considered weight-neutral, meaning they do not usually cause weight gain or weight loss. This makes them a suitable option for individuals who want to manage their blood sugar without affecting their weight.
Convenience: DPP-4 inhibitors are typically taken once a day, offering a simple and convenient treatment routine. This daily dosing schedule makes it easier for patients to stick with their diabetes medications and maintain consistent blood sugar control.
Side Effects:
Mild Gastrointestinal Issues: Some patients may experience mild nausea or abdominal discomfort.
Pancreatitis Risk: Though rare, DPP-4 inhibitors have been associated with an increased risk of pancreatitis.
Ideal For: People with Type 2 diabetes who require additional control of blood glucose but do not need more aggressive treatment.
SGLT-2 Inhibitors
Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors are a newer type of diabetes medications used to manage Type 2 diabetes. These medications work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose back into the bloodstream. Instead, excess sugar is removed from the body through urine, helping to lower blood sugar levels. SGLT-2 inhibitors offer an effective option for individuals who need additional support beyond traditional diabetes medications, and they may also provide added benefits for heart and kidney health in some patients.
Mechanism of Action: SGLT-2 inhibitors block the SGLT-2 protein in the kidneys, which is responsible for reabsorbing glucose back into the blood. By inhibiting this protein, excess glucose is excreted in the urine, thus lowering blood glucose levels.
Common Medications:
Canagliflozin (Invokana)
Dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
Empagliflozin (Jardiance)
Benefits:
Weight Loss: SGLT-2 inhibitors can support weight loss by helping the body eliminate excess glucose through urine. This loss of glucose means fewer calories are absorbed, which may lead to modest weight reduction over time. This added benefit makes these diabetes medications appealing for individuals looking to manage both blood sugar and weight.
Cardiovascular and Renal Benefits: In addition to lowering blood sugar, SGLT-2 inhibitors have shown positive effects on heart and kidney health. These diabetes medications can reduce the risk of heart failure and slow the progression of chronic kidney disease in people with Type 2 diabetes.
Lower Risk of Hypoglycemia: SGLT-2 inhibitors do not work by increasing insulin production. As a result, they carry a lower risk of causing hypoglycemia, or dangerously low blood sugar levels, making them a safer choice for some patients using diabetes medications.
Side Effects:
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Increased glucose in the urine can provide a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to higher UTI risk.
Dehydration and Low Blood Pressure: SGLT-2 inhibitors can cause dehydration and hypotension due to increased urination.
Ideal For: Patients with Type 2 diabetes who have heart disease, kidney disease, or are at high risk for cardiovascular events.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are a type of injectable diabetes medications used to treat Type 2 diabetes. These drugs work by mimicking the action of GLP-1, a natural hormone in the body that helps regulate blood sugar levels. GLP-1 receptor agonists increase insulin production when blood sugar is high, slow down digestion, and reduce the release of sugar from the liver. These diabetes medications offer effective blood sugar control and may also support weight loss and heart health in some individuals.

Mechanism of Action: GLP-1 receptor agonists increase insulin secretion in response to meals, inhibit glucagon release (which helps prevent the liver from producing excess glucose), and slow gastric emptying, which can promote satiety.
Common Medications:
Liraglutide (Victoza)
Exenatide (Byetta)
Semaglutide (Ozempic)
Benefits:
Weight Loss: GLP-1 receptor agonists are known to support weight loss in many individuals with Type 2 diabetes. These diabetes medications help reduce appetite by affecting areas of the brain that control hunger, leading to lower calorie intake and gradual weight reduction over time.
Cardiovascular Benefits: Some GLP-1 receptor agonists have shown positive effects on heart health. These diabetes medications may help lower the risk of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, offering added protection for people with existing heart conditions.
Low Risk of Hypoglycemia: When used alone, GLP-1 receptor agonists have a low chance of causing hypoglycemia, or dangerously low blood sugar levels. This is because these diabetes medications only stimulate insulin release when blood sugar is elevated, making them a safer option for many patients.
Side Effects:
Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea are common, especially when starting treatment.
Pancreatitis Risk: There is a slight risk of pancreatitis with GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Ideal For: Type 2 diabetes patients who are overweight and need both blood sugar control and weight management.
Insulin
Insulin therapy is a critical part of treatment for individuals with Type 1 diabetes, as their bodies do not produce insulin naturally. It is also used in cases of Type 2 diabetes when blood sugar levels cannot be managed effectively with other diabetes medications. Insulin helps regulate blood sugar by allowing glucose to enter cells for energy. For some people, adding insulin to their treatment plan is necessary to achieve better blood sugar control and prevent diabetes-related complications over time.
Mechanism of Action: Insulin replaces or supplements the body’s own insulin, allowing glucose to enter cells and be used as energy. It is injected subcutaneously (under the skin) and comes in several formulations, including rapid-acting, long-acting, and intermediate-acting types.
Common Insulin Types:
Rapid-Acting Insulin (e.g., Humalog, Novolog)
Long-Acting Insulin (e.g., Lantus, Levemir)
Benefits:
Effective for Blood Sugar Control: Insulin remains one of the most effective methods for lowering blood sugar levels, especially in individuals with Type 1 diabetes who rely on it for survival. It helps move glucose from the blood into the body’s cells, keeping blood sugar within a healthy range. Among all diabetes medications, insulin provides the most direct and powerful control of blood glucose levels.
Flexible Dosing: One of the key advantages of insulin therapy is its flexibility. Doses can be adjusted based on factors like meals, activity levels, and blood sugar readings, allowing for a highly personalized treatment plan. This makes insulin one of the most adaptable diabetes medications, tailored to fit each person’s specific health needs and lifestyle.
Side Effects:
Hypoglycemia: If too much insulin is taken, or meals are missed, hypoglycemia can occur.
Weight Gain: Some insulin therapies can lead to weight gain over time.
Ideal For: Individuals with Type 1 diabetes and those with Type 2 diabetes who have inadequate blood sugar control with oral medications.
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs)
Thiazolidinediones are a class of diabetes medications used to treat Type 2 diabetes by improving the body’s sensitivity to insulin. These drugs work by helping muscle and fat cells respond better to insulin, which allows glucose to enter the cells more easily. As a result, blood sugar levels can be lowered effectively. Thiazolidinediones are often prescribed when other diabetes medications are not enough to achieve proper blood sugar control. They offer another treatment option for managing long-term glucose levels in Type 2 diabetes.
Mechanism of Action: TZDs work by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which improve insulin sensitivity in muscle and fat cells, allowing them to use glucose more effectively.

Common Medications:
Pioglitazone (Actos)
Rosiglitazone (Avandia)
Benefits:
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) work by increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin, making it easier for cells to absorb and use glucose. This helps lower blood sugar levels more effectively in people with Type 2 diabetes. These diabetes medications are especially helpful for those who have insulin resistance.
Cardiovascular Benefits: Among TZDs, pioglitazone has shown potential heart-related benefits. Some studies suggest that it may help lower the risk of heart disease in people with Type 2 diabetes, offering an added advantage beyond regular blood sugar control with diabetes medications.
Side Effects:
Weight Gain: TZDs may cause fluid retention and weight gain.
Bone Fractures: Long-term use may increase the risk of bone fractures.
Heart Failure: TZDs may exacerbate heart failure in some individuals.
Ideal For: Type 2 diabetes patients who need improvement in insulin sensitivity but cannot tolerate other medication classes.
Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are a type of oral diabetes medications used to manage Type 2 diabetes. These drugs work by slowing down the breakdown and absorption of carbohydrates in the small intestine. As a result, they help reduce the sharp rise in blood sugar levels that often occurs after eating a meal. By targeting post-meal glucose spikes, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors provide another effective way to maintain better overall blood sugar control. They are often used alongside other diabetes medications for improved results.
Common Medications:
Acarbose (Precose)
Miglitol (Glyset)
Mechanism of Action: These medications work by inhibiting enzymes in the intestines that break down carbohydrates into glucose. As a result, the absorption of glucose is slowed, preventing sharp spikes in blood sugar after meals.
Benefits:
Post-Meal Blood Sugar Control: These medications are especially effective at reducing blood sugar spikes that occur after meals.
Minimal Risk of Hypoglycemia: They do not increase insulin levels, so they do not cause low blood sugar on their own.
Side Effects:
Gastrointestinal Issues: Gas, bloating, and diarrhea are common side effects due to the undigested carbohydrates in the intestines.
Ideal For: Type 2 diabetes patients who struggle with high blood sugar after meals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing diabetes effectively requires a combination of lifestyle modifications and the appropriate use of diabetes medications. From the commonly prescribed metformin to newer options like SGLT-2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists, each medication serves a specific purpose in controlling blood sugar and improving insulin sensitivity. While Type 1 diabetes often necessitates insulin therapy, individuals with Type 2 diabetes may benefit from a variety of oral and injectable medications that target different aspects of glucose regulation.

It’s essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the most effective treatment plan based on their unique health profile and needs. By doing so, people with diabetes can manage their condition more effectively, reduce the risk of complications, and maintain a better quality of life. Understanding and utilizing the right diabetes medications is crucial in the ongoing effort to control blood sugar and promote long-term health.
FAQs
What are the most common medications for Type 2 diabetes ?
The most common medications include metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, SGLT-2 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists.
How do diabetes medications work ?
Diabetes medications work by either increasing insulin production, improving insulin sensitivity, or reducing glucose production, depending on the drug class.
Can diabetes medications cause weight gain ?
Some diabetes medications, such as sulfonylureas and insulin, may cause weight gain, while others like GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT-2 inhibitors may promote weight loss.
Do diabetes medications cause hypoglycemia ?
Medications like sulfonylureas and insulin may cause low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), while drugs like DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 agonists have a lower risk.
When should I start taking diabetes medications ?
Diabetes medications are typically prescribed when lifestyle changes alone (diet and exercise) are insufficient to control blood sugar levels. Your doctor will determine the best time to start based on your individual condition.

