Chronic pain affects millions of people globally, severely impacting daily life and overall well-being. While medications can offer temporary relief, long-term use often leads to dependency, tolerance, and various side effects. This makes it essential to explore alternative, non-pharmacological methods for managing pain.
Thankfully, many natural strategies have proven effective in relieving chronic pain sustainably. These approaches not only help alleviate discomfort but also promote overall health and healing. From physical therapies to lifestyle changes, there are various ways to manage pain without relying on medications.
By including effective methods such as exercise, meditation, and dietary adjustments, you can take a more active role in managing your pain. These techniques provide lasting benefits without the risks associated with long-term medication use, allowing you to enhance your quality of life and regain control over your health.
Understanding Chronic Pain
What is Chronic Pain ?
Chronic pain is persistent pain lasting over three months. Unlike acute pain, which typically indicates injury or illness, chronic pain can persist long after recovery, often without a clear cause. This ongoing discomfort can significantly impact daily life and well-being, making it more challenging to manage.
Common Causes of Chronic Pain:
Arthritis and joint disorders
Fibromyalgia
Back and neck injuries
Neuropathic pain (nerve damage)
Post-surgical or trauma-related pain
Inflammatory conditions
Physical Therapy and Exercise

- Benefits of Movement
Regular movement plays an important role in keeping the joints flexible, improving blood circulation, and helping to lower inflammation in the body. Staying active prevents stiffness and can make daily activities easier and less painful. Physical therapy offers a personalized plan with specific exercises that focus on the areas where pain is most common. These exercises help to build strength, improve balance, and increase overall mobility, making it easier to manage chronic pain over time.
Recommended Practices:
Low-Impact Aerobics: Activities like swimming, walking, and cycling are gentle on the joints while helping to improve heart health and overall endurance. They also boost circulation, which can help ease chronic pain without putting too much pressure on the body.
Stretching and Flexibility: Regular stretching exercises help keep the muscles and joints flexible, making movement easier and more comfortable. Stretching can also reduce stiffness and lower the risk of further injury or strain.
Strength Training: Building stronger muscles through strength training provides better support for the joints. This can help reduce strain on painful areas, improve stability, and make daily tasks less challenging.
Tip: Always consult a physical therapist before starting an exercise regimen tailored to your condition.
Mind-Body Techniques
- The Mind-Pain Connection
Our experience of pain is shaped by emotional, psychological, and neurological factors. Feelings like stress, anxiety, and sadness can make pain feel more intense and harder to manage. Mind-body techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, and guided imagery, help calm the mind and body. These methods lower stress levels and teach the brain to process pain signals in a healthier way, making pain feel less overwhelming over time.
Popular Mind-Body Practices:
Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness meditation helps increase awareness of the present moment and can lower the intensity of pain. It teaches you to observe pain without reacting strongly to it, which can make it feel more manageable.
Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing helps calm the nervous system and reduce the body’s stress response. By slowing down your breathing, you can relax your muscles and lower feelings of pain and tension.
Yoga and Tai Chi: These gentle practices combine slow movements, controlled breathing, and mindfulness. They help improve flexibility, balance, and strength while also promoting relaxation, all of which can help ease chronic pain.
Biofeedback: Biofeedback is a technique that teaches you to control certain body functions, like heart rate and muscle tension. By learning to adjust these responses, you can better manage pain and reduce physical stress on your body.
Case Study: Studies from Harvard Medical School show that mindfulness can significantly reduce pain perception and improve quality of life.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT
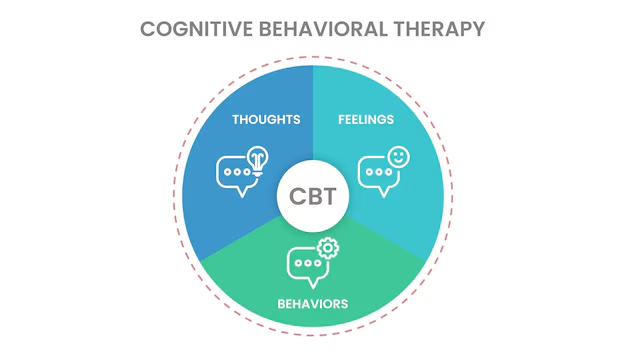
- Rewiring Thought Patterns
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors that can make pain feel worse. It teaches healthier ways to respond to pain, leading to better emotional and physical well-being. CBT offers long-term benefits for managing chronic pain naturally, without the risk of side effects.
How CBT Helps:
Helps lower anxiety and depression linked to pain
Strengthens coping skills for managing discomfort
Promotes positive changes in daily habits and behaviours
SEO Keyword Tip: Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Chronic Pain is a trending keyword—make sure to include this in web content targeting pain sufferers.
Acupuncture and Acupressure
- Ancient Wisdom for Modern Relief
Acupuncture, a practice from Traditional Chinese Medicine, involves gently inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. This method aims to rebalance the body’s natural energy flow and encourage healing. Many people use acupuncture to help relieve pain, improve relaxation, and support overall health and well-being.
Benefits of Acupuncture:
Promotes natural pain relief (endorphin release)
Reduces inflammation and improves circulation
Enhances overall well-being
Acupressure, a needle-free alternative, uses finger pressure on meridian points to achieve similar outcomes.
Pro Tip: It’s important to always choose a certified and experienced practitioner when considering acupuncture. A qualified professional will ensure that the treatment is done safely, using proper techniques and sterile equipment. This helps you get the best results while minimizing any risks of infection or injury during the session.
Diet and Nutrition

- Food as Medicine
Inflammation is a key factor in chronic pain, often making symptoms worse. Following a balanced, anti-inflammatory diet can help lower inflammation in the body, leading to reduced pain over time. Eating whole foods like fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats supports healing and promotes long-term relief from discomfort.
Pain-Fighting Nutrients:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids (salmon, flaxseed)
Antioxidants (berries, spinach, green tea)
Magnesium (almonds, bananas, leafy greens)
Vitamin D (sunlight, fortified foods)
Foods to Avoid:
Processed sugars and carbohydrates
Trans fats and deep-fried foods
Excessive alcohol and caffeine
SEO Tip: Include keywords like “Anti-Inflammatory Diet for Chronic Pain” in blog content.
Heat and Cold Therapy
- Easy, At-Home Pain Relief
Using a combination of heat and cold therapy can be an effective way to manage pain and reduce inflammation. Heat relax
How It Works:
Heat Therapy: Applying heat to painful areas helps increase blood circulation, which promotes healing and relaxation. It also helps loosen tight muscles, easing stiffness and discomfort. Heat is especially beneficial for chronic muscle pain, joint pain, and conditions like arthritis.
Cold Therapy: Cold therapy helps reduce sharp pain by numbing the affected area, providing immediate relief. It also helps reduce swelling and inflammation by constricting blood vessels, making it effective for acute injuries, sprains, and conditions where inflammation is the primary concern.
Best Practices:
Use heating pads or warm baths for 15–20 minutes
Apply ice packs for acute flare-ups
Avoid direct contact with skin to prevent burns or frostbite
Massage Therapy
- Healing Through Touch
Massage therapy helps improve blood circulation, reducing muscle tension and promoting overall relaxation. By relieving tightness and increasing blood flow to affected areas, it effectively reduces pain and enhances healing. Regular massage can be a valuable part of managing chronic pain and improving physical well-being.
Types of Massage for Pain:
Swedish Massage: Gentle and soothing
Deep Tissue Massage: Targets deeper muscle layers
Trigger Point Therapy: Focuses on specific pain points
Quick Fact: A 2021 study from the Mayo Clinic confirmed that weekly massages helped reduce chronic back pain in over 70% of participants.
Sleep Hygiene and Restorative Sleep
- The Pain-Sleep Connection
Lack of quality sleep can increase pain sensitivity and make chronic pain feel more intense. Prioritizing restful, restorative sleep helps reduce pain perception, allowing the body to recover and heal. Consistently getting good sleep can greatly improve chronic pain symptoms, promoting better overall well-being and comfort.
Sleep Improvement Tips:
Stick to a regular sleep schedule
Avoid screens and heavy meals before bed
Use white noise machines or blackout curtains
Consider natural supplements like melatonin or valerian root
Support Groups and Social Connection

Support groups provide a safe and understanding space for people with chronic pain to share their experiences, challenges, and coping techniques. These groups — whether in-person or online — offer a sense of community that can:
Validate personal experiences: Connecting with others who share similar struggles helps lessen feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Offer emotional support: Group members often provide understanding and empathy that even close family or friends might not be able to offer.
Exchange practical advice: Peers can share valuable tips on managing pain and navigating healthcare systems, offering practical solutions.
Build hope and resilience: Hearing stories of people who have successfully adapted to chronic pain can inspire and encourage you to stay positive and resilient.
Conclusion
Chronic pain can be overwhelming, but natural methods can provide lasting relief without the risks of long-term medication use. Incorporating practices like exercise, mindfulness, nutrition, and social support allows you to take an active role in managing your pain. These strategies help you address both the physical and emotional aspects of pain.
Everyone’s body responds differently, so it’s important to be patient with yourself as you explore different approaches. Finding what works best for you may take time, but by being open to various methods, you can develop a personalized plan that supports your needs.
With dedication and the right tools, it’s possible to regain control over your health. A holistic approach to pain management can not only help reduce discomfort but also improve your overall well-being. By taking charge of your health, you can live a more comfortable and empowered life, despite the challenges of chronic pain.
FAQs
- What is chronic pain?
Chronic pain is pain that lasts longer than three months, often persisting even after an injury or illness has healed. It can occur without a clear cause and can affect daily life and overall well-being. - What causes chronic pain ?
Chronic pain can be caused by various factors, including past injuries, underlying medical conditions (such as arthritis or fibromyalgia), nerve damage, and inflammation. Sometimes, the cause of chronic pain is unknown. - How can I manage chronic pain without medication ?
Non-medical strategies like exercise, physical therapy, mindfulness, yoga, acupuncture, and proper sleep can help manage chronic pain. Stress reduction techniques and a healthy diet also play important roles in pain relief. - Is chronic pain psychological ?
While chronic pain has a physical basis, emotional and psychological factors, such as stress, depression, and anxiety, can worsen pain perception. Mind-body techniques, such as cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT), can help manage these effects. - Can chronic pain ever be cured?
Chronic pain can often be managed, but it may not always be fully curable. With proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments, many people can significantly reduce their pain and improve their quality of life.

