Elbow joint pain is a prevalent musculoskeletal issue that affects individuals across all age groups. It often arises due to repetitive strain, overuse, injuries, or underlying conditions such as arthritis or inflammation. The elbow is a hinge joint connecting the upper arm to the forearm, enabling movements like bending, straightening, and rotation. When this joint experiences pain, everyday tasks such as typing, lifting objects, or playing sports can become challenging, reducing overall productivity and quality of life. Addressing elbow joint pain early is essential to prevent chronic discomfort and maintain functional mobility.
Understanding the causes of elbow joint pain is crucial for effective management. Common triggers include tendonitis, bursitis, fractures, or nerve compression. Recognizing the symptoms—such as swelling, stiffness, weakness, or tingling—allows for timely intervention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and promote quicker recovery.
Effective remedies for elbow joint pain include rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory measures, ergonomic adjustments, and, in severe cases, medical interventions. Incorporating targeted exercises, proper nutrition, and supportive devices like braces can significantly alleviate discomfort and improve joint strength. By adopting preventive strategies and consistent care, individuals can manage elbow pain effectively and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.

What is Elbow Joint Pain ?
Elbow joint pain refers to discomfort, soreness, or tenderness around the elbow, affecting its normal function. It can be acute, resulting from a sudden injury, or chronic, developing gradually due to repetitive motions, overuse, or degenerative conditions. The pain may be localized to the inner, outer, or back side of the elbow, sometimes accompanied by swelling, stiffness, or a reduced range of motion.
Several common conditions contribute to elbow joint pain. Tennis elbow, caused by overuse of the forearm muscles, leads to pain on the outer elbow, while golfer’s elbow affects the inner side. Bursitis involves inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs that cushion the elbow, causing swelling and tenderness. Osteoarthritis results from wear and tear of the joint cartilage, leading to chronic pain and stiffness.
Identifying the underlying cause of elbow pain is essential for effective management. Proper diagnosis allows for targeted treatments such as rest, physical therapy, medications, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention. Early intervention can prevent further damage and promote faster recovery.
How Does Elbow Joint Pain Occur
Elbow joint pain occurs when stress, injury, or inflammation affects the joint’s bones, tendons, or ligaments. Repetitive activities like typing, lifting, or playing racquet sports strain tendons and muscles, causing conditions such as tennis or golfer’s elbow. Inflammation and microtears in tissues trigger pain signals. Over time, chronic stress can weaken the joint, reducing mobility and causing stiffness.
Arthritis, bursitis, and nerve compression also contribute to elbow joint pain. Arthritis gradually erodes cartilage, while bursitis inflames the protective fluid-filled sacs, leading to swelling and discomfort. Nerve compression in the elbow can cause tingling or numbness, adding to pain.
Additionally, sudden trauma like fractures, dislocations, or direct impacts can instantly damage bones and soft tissues, resulting in acute elbow joint pain. Understanding how elbow pain develops helps in selecting preventive measures, treatments, and rehabilitation exercises to restore joint function and reduce discomfort.
Why Elbow Joint Pain Occurs
Elbow joint pain occurs due to a variety of factors that affect the bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments around the elbow. Overuse is one of the most common causes, especially in activities requiring repetitive motion like typing, lifting, or sports such as tennis and golf. Repeated stress can cause microtears in the tendons and muscles, leading to inflammation, stiffness, and discomfort. Chronic overuse without proper rest can worsen the condition and lead to long-term elbow joint pain.
In addition to overuse, degenerative conditions like arthritis contribute significantly to elbow joint pain. Arthritis gradually wears down the protective cartilage, causing the bones to rub against each other. This friction results in swelling, pain, and reduced mobility. Other inflammatory conditions, including bursitis or tendonitis, trigger immune responses in the joint area, intensifying pain and limiting function.
Injury and trauma are also key reasons for elbow joint pain. Fractures, dislocations, or direct impacts can damage bones and soft tissues. Nerve compression or irritation around the elbow can cause tingling, numbness, or radiating pain down the forearm. Understanding why elbow joint pain occurs is crucial to prevent further injury and apply effective treatment strategies.
Causes of Elbow Joint Pain
Overuse Injuries – Repetitive movements, such as typing, weightlifting, or racquet sports, strain muscles and tendons around the elbow.
Arthritis – Osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation, stiffness, and chronic pain.
Bursitis – Inflammation of the bursa (fluid-filled sac) near the elbow, often caused by trauma or pressure.
Tendonitis – Tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis) or golfer’s elbow (medial epicondylitis) results from inflammation of tendons.
Fractures and Dislocations – Trauma or falls may lead to severe pain and mobility restrictions.
Nerve Compression – Ulnar nerve entrapment can cause pain, tingling, or numbness in the elbow and forearm.
Symptoms of Elbow Joint Pain
Localized pain, sometimes radiating to forearm or upper arm
Swelling or redness around the joint
Stiffness, difficulty in bending or straightening the arm
Weak grip strength
Tingling or numbness if nerves are affected
Top Tips to Manage Elbow Joint Pain
Rest and Avoid Overuse

Resting the elbow is crucial in managing elbow joint pain. Overuse, such as repeated lifting, typing, or heavy physical activity, strains the joint and surrounding muscles, leading to inflammation. Allowing the elbow proper rest prevents further damage and gives tendons and ligaments time to heal. Incorporating short breaks during repetitive tasks reduces cumulative stress and accelerates recovery.
In addition to rest, adjusting your workspace ergonomically can significantly reduce strain. Using an appropriate keyboard, mouse, and chair, along with maintaining proper posture, alleviates pressure on the elbow joint. For athletes or manual laborers, limiting repetitive motions and spacing out activities can prevent aggravation of elbow pain.
Supporting tools like elbow braces or cushioned sleeves provide stability while allowing mobility during daily tasks. These simple measures, when combined with rest, form the foundation of effective elbow pain management, preventing flare-ups and promoting faster healing.
Benefits:
Reduces inflammation
Prevents further injury
Speeds up recovery
Ingredients for Rest:
Elbow braces or sleeves
Cushioned supports
Adjusted workspace ergonomics
Apply Ice or Heat Therapy
Ice and heat therapy are highly effective in alleviating elbow joint pain. Ice packs reduce swelling and numb acute pain during the first 24–48 hours of injury or inflammation. Applying ice for 15–20 minutes several times a day constrains tissue damage and minimizes discomfort. After initial inflammation subsides, heat therapy can relax stiff muscles and increase blood circulation to promote healing.
Alternating between cold and heat therapy accelerates tissue repair and improves flexibility. Ice or cold packs are ideal for acute flare-ups, whereas heat packs or warm compresses are better for chronic stiffness. This combination improves the mobility of the elbow joint and relieves discomfort from overuse or arthritis-related elbow pain.
Consistent application of ice and heat ensures sustained relief. Wrapping packs in a soft towel prevents skin damage. Integrating this therapy into your routine provides a non-invasive method to manage elbow joint pain effectively.
Benefits:
Reduces swelling and inflammation
Relieves soreness and stiffness
Promotes blood circulation
Ingredients for Therapy:
Ice packs or frozen gel packs
Warm compress or heating pad
Soft towels
Physical Therapy and Stretching
Physical therapy plays a critical role in alleviating elbow joint pain. Targeted exercises strengthen the forearm muscles, biceps, triceps, and wrist extensors, reducing strain on the elbow. Stretching routines help restore flexibility, improve range of motion, and prevent stiffness caused by prolonged immobilization.
A physiotherapist can design a personalized program, including resistance band exercises, light weights, and guided stretches. Regular practice enhances joint stability and promotes recovery from injuries such as tendonitis, bursitis, or post-surgical stiffness. Strengthening surrounding muscles ensures long-term support for the elbow, lowering the risk of recurrence of elbow pain.
In addition to exercises, integrating stretching into daily routines before and after activity reduces stress on the joint. Stretching improves blood flow, reduces tightness, and supports tendon and ligament health. Physical therapy combined with mindful movement offers a holistic approach to managing elbow pain naturally.
Benefits:
Enhances joint mobility
Strengthens supporting muscles
Prevents chronic pain
Physical Therapy Ingredients:
Resistance bands
Light weights
Stretching mats
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Medications such as NSAIDs can provide temporary relief from elbow joint pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling. Topical creams or gels can be applied directly to the affected area for targeted relief, especially for those experiencing arthritis or tendonitis.
However, long-term or excessive use can lead to side effects, so consulting a healthcare professional is crucial. Medications serve as a supportive measure in conjunction with rest, therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage elbow joint pain effectively. They are particularly helpful during acute flare-ups or when performing physical therapy exercises.
Using medications strategically, combined with other treatment methods like ergonomic adjustments and exercise, provides a comprehensive approach. Proper usage ensures that elbow pain is controlled while minimizing adverse effects.
Benefits:
Reduces pain and inflammation
Improves daily function
Supports recovery
Medication Ingredients:
NSAID tablets or gels
Prescription anti-inflammatories (if needed)
Topical analgesics
Use Supportive Braces or Straps
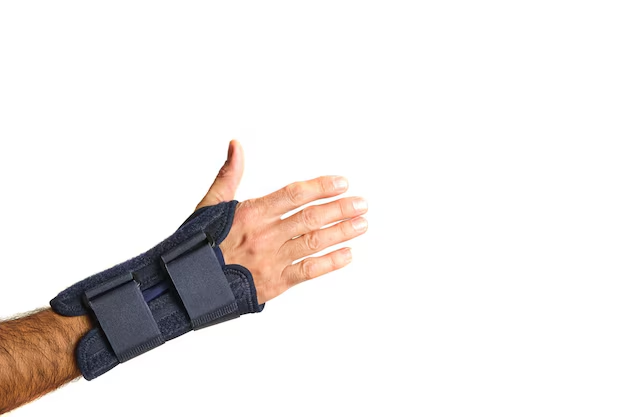
Supportive devices such as elbow braces or compression sleeves stabilize the joint and relieve elbow joint pain. Tennis elbow straps specifically reduce tension on the lateral epicondyle, while general sleeves provide warmth and compression to inflamed areas. Braces allow functional movement while protecting the joint from excessive strain.
These tools are beneficial during work, sports, or daily activities that involve repetitive motions. By reducing stress on tendons and muscles, braces prevent flare-ups and support healing. They are especially effective for chronic conditions like tennis or golfer’s elbow.
Consistent use of supportive gear ensures long-term management of elbow pain, while also enabling patients to remain active. Pairing braces with physical therapy enhances joint stability and overall recovery.
Benefits:
Reduces stress on tendons and muscles
Provides stability
Supports healing while performing light tasks
Support Ingredients:
Tennis elbow strap
Compression sleeves
Adjustable elbow braces
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Nutrition plays a key role in preventing and managing elbow joint pain. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods like fatty fish, leafy greens, citrus fruits, nuts, and whole grains helps reduce inflammation and supports joint health. Omega-3 fatty acids, calcium, vitamin D, and antioxidants strengthen bones, tendons, and ligaments.
Proper nutrition accelerates tissue repair, maintains bone density, and prevents degeneration of cartilage. A balanced diet also supports overall wellness, contributing to reduced elbow pain and improved physical performance.
Hydration, along with adequate protein intake, further supports tendon repair and muscle recovery. Consistently eating nutrient-dense meals complements other treatments such as therapy, braces, and medications to provide comprehensive care for elbow pain.
Benefits:
Reduces inflammation naturally
Supports bone and tendon health
Improves overall wellness
Diet Ingredients:
Salmon, mackerel
Spinach, kale, broccoli
Almonds, walnuts
Oranges, berries
Alternative Therapies
Alternative therapies like acupuncture, massage, and hydrotherapy can complement conventional treatments for elbow pain. Acupuncture targets pressure points to alleviate pain and inflammation, while massage improves circulation, reduces stiffness, and relaxes surrounding muscles. Hydrotherapy with warm water exercises gently enhances mobility and reduces joint stress.
These therapies are especially beneficial for chronic pain, repetitive strain injuries, or post-surgical rehabilitation. Combining alternative methods with physical therapy enhances recovery and provides relaxation, improving the patient’s overall well-being.
Regular sessions can improve circulation, reduce discomfort, and restore functional movement. Integrating alternative therapies ensures a multi-faceted approach to managing elbow pain, supporting both physical and mental health during recovery.
Benefits:
Alleviates chronic pain
Improves blood flow
Enhances relaxation
Alternative Therapy Ingredients:
Licensed acupuncturist or therapist
Massage oils or gels
Warm water pools
Surgical Options (If Required)
In severe or persistent cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to address elbow pain. Procedures such as tendon repair, arthroscopy, or partial joint replacement are considered when conservative treatments fail. Surgery is usually reserved for chronic tendon tears, advanced arthritis, or fractures that impair function.
Post-surgery rehabilitation is critical for regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Physical therapy, along with pain management protocols, ensures optimal recovery and prevents recurrence. Early detection and proper surgical planning improve outcomes and minimize complications associated with elbow joint pain.
Surgical solutions, combined with lifestyle adjustments, diet, and preventive measures, provide a comprehensive strategy for long-term joint health. Patients who follow a structured post-op plan often regain full mobility and experience minimal discomfort from elbow pain.
Benefits:
Repairs damaged tendons or joints
Reduces chronic pain
Restores mobility
Surgical Ingredients:
Orthopedic surgeon consultation
Pre- and post-op physiotherapy
Pain management protocols
Prevention of Elbow Joint Pain
Preventive measures are essential to avoid future pain. Avoid repetitive strain, maintain proper ergonomics at work, and strengthen muscles around the elbow. Stretch before and after physical activities, use protective gear in sports, and maintain a balanced diet for bone and joint health.
Conclusion

Elbow joint pain can greatly impact daily activities, making simple tasks like lifting, typing, or playing sports difficult. Understanding the underlying causes, such as overuse, tendon inflammation, arthritis, or nerve compression, is essential for effective management. Early identification allows individuals to take preventive measures and address the pain before it becomes chronic. Awareness of risk factors and symptoms also helps in choosing the right treatment approach, reducing long-term joint complications.
Core strategies for managing elbow pain include rest, physical therapy, and anti-inflammatory treatments. Resting the joint prevents further strain, while targeted exercises improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion. Using braces or supports can stabilize the elbow during daily activities. Anti-inflammatory medications or topical treatments reduce swelling and discomfort, while maintaining a nutritious diet rich in omega-3s, vitamins, and minerals supports tissue repair and overall joint health.
For chronic or severe conditions, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures like tendon repair or arthroscopy restore joint function and relieve persistent pain. Regular monitoring, preventive care, and adopting healthy lifestyle practices ensure long-term elbow health. By following these strategies consistently, individuals can manage elbow joint pain effectively, improve mobility, and maintain an active, pain-free lifestyle.
FAQs
Q1. What are common causes of elbow joint pain ?
Elbow joint pain can arise from a variety of factors affecting the muscles, tendons, ligaments, bones, or nerves around the joint. Overuse is one of the most common causes, especially in repetitive activities like typing, lifting weights, or playing sports such as tennis and golf.
Q2. Can elbow pain heal naturally without surgery ?
Yes, many instances of elbow joint pain can improve naturally without surgical intervention. The key lies in rest, avoiding activities that aggravate the joint, and adopting proper ergonomics in daily tasks. Physical therapy is highly effective, as it strengthens surrounding muscles, improves flexibility, and restores range of motion.
Q3. Are braces effective for elbow joint pain ?
Yes, braces or supportive straps are an important non-invasive tool for managing elbow joint pain. They stabilize the joint, reduce strain on inflamed tendons, and allow the elbow to heal while maintaining functionality for light daily activities.
Q4. Which foods help in elbow joint pain ?
Nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting joint health and managing elbow joint pain. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, mackerel, and walnuts, help reduce inflammation in tendons and joints. Vitamin C (citrus fruits, berries) and vitamin D (fortified dairy, sunlight exposure) promote tissue repair and bone health.
Q5. When should I see a doctor for elbow pain ?
Medical attention is recommended for elbow joint pain if symptoms are severe, persistent, or worsening over time. Other warning signs include swelling, redness, warmth around the joint, inability to fully extend or flex the elbow, or pain that limits daily activities like lifting, typing, or sports participation.

